Understanding How Speedtest Websites Work and Factors Affecting Their Results
In the digital age, where our reliance on the internet is ever-growing, the performance of our internet connection has become a critical aspect of daily life. Whether it’s for work, streaming, gaming, or simply browsing, knowing the speed of your internet connection is essential. Speedtest websites like speedtest.net, testmyspeed.com, fast.com. and many others, have emerged as a popular tools for measuring internet performance. But! Have you ever wondered how these tests work, what can affect their accuracy, and furthermore – are they even accurate to begin with? This blog delves into the mechanics of speedtest websites and explores various factors that can impact their results.
How Speedtest Websites Work
The Basics of Speed Testing
Speedtest websites are designed to measure three primary metrics of your internet or network connection:
- Download Speed: The rate at which data is received from the internet to your device.
- Upload Speed: The rate at which data is sent from your device to the internet.
- Latency (Ping): The time it takes for a data packet to travel from your device to a server and back, measured in milliseconds (ms).
The Testing Process
When you initiate a speed test, the website performs the following steps:
-
Server Selection: The speedtest website selects a nearby server to conduct the test. This is often a server maintained by the speedtest provider.
-
Ping Test: The website measures the latency by sending a small amount of data to the server and measuring the round-trip time. This gives a preliminary indication of the responsiveness of your connection.
-
Download Test: The website begins transferring data from the server to your device. This involves downloading a large file or a stream of data in a short time span. The speed at which this data is downloaded is measured and reported as your download speed.
-
Upload Test: Similarly, the website uploads data from your device to the server. This involves sending a large file or a stream of data to the server. The speed at which this data is uploaded is measured and reported as your upload speed.
-
Analysis and Reporting: Once the tests are complete, the website analyzes the data, calculates the average speeds and latency, and presents the results to you.
Factors Affecting Speedtest Results
While speedtest websites are a useful tool for gauging your internet performance, several factors can influence the accuracy and reliability of the results:
1. Network Congestion
-
Local Network Traffic: If multiple devices are using the internet simultaneously within your local network (e.g., for streaming, gaming, or large downloads), it can impact the available bandwidth for the speed test. This can result in lower speeds than what your Internet Service Provider (ISP) is providing you under optimal conditions.
-
ISP’s Network Traffic: During peak usage times, there may be high traffic on your ISP’s network, affecting your internet speeds. This congestion can impact the speed test results.
-
SpeedTest Provider’s Network Traffic: During peak testing times, the speedtest server may experience delays due to high demand and deliver inaccurate results.
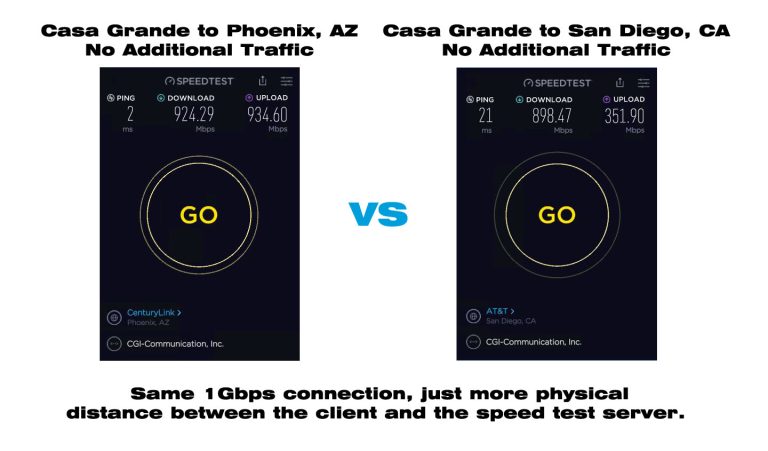
2. Server Proximity
-
Distance from Server: The physical distance between your device and the test server can affect the results. Greater distances can introduce additional latency and may result in lower speeds due to increased travel time for data packets. Not to mention other providers networks in between your device and the speedtest server.
-
Server Load: The performance of the test server itself can influence the results. If the server is overloaded or experiencing high traffic, it may not be able to handle the test efficiently, leading to inaccurate results.
3. Hardware Limitations
-
Router/Modem Performance: The capabilities of your router and modem can impact your speedtest results. Older or less capable hardware may not be able to handle high-speed connections effectively, leading to lower reported speeds.
-
Device Specifications: The performance of the device used for the test can also affect the results. Older devices, failing hardware, or those with limited processing power may struggle to handle high-speed connections and may not accurately reflect your internet speed.
4. Network Interference
-
Wi-Fi vs. Wired Connection: Wi-Fi connections are subject to interference from other wireless devices, walls, and distance. A wired connection (Ethernet) generally provides more stable and accurate results as it is less prone to interference.
-
Interference Sources: Other electronic devices, such as cordless phones, microwaves, or neighboring Wi-Fi networks, can interfere with your Wi-Fi signal, potentially affecting speedtest results.
5. ISP Throttling
- Bandwidth Throttling: Some ISPs (not CGI) implement throttling to manage network congestion or enforce data usage policies. This can result in slower speeds during certain times or for specific types of traffic. Speedtest results may be affected if throttling is in place.
6. Background Applications
- Ongoing Downloads/Uploads: If other applications or services are using bandwidth during the test (such as file downloads, cloud backups, cloud based security cameras, or video streaming), it can impact the speedtest results. Ensure that no other significant network activity is occurring during the test for more accurate results. Consider connecting only one device directly to the provider for the most accurate results.
Conclusion
Speedtest websites are valuable tools for assessing your internet connection’s performance, but it’s essential to understand the factors that can influence the results. Network congestion, server proximity, hardware limitations, network interference, ISP throttling, and background applications can all affect the accuracy of your speedtest results. By considering these factors and performing multiple tests under different conditions, you can gain a more comprehensive understanding of your internet connection’s true performance.
For the most accurate results, it’s recommended to conduct speed tests at different times of the day, use a wired connection if possible, and ensure that no other significant network activity is occurring. By taking these precautions, you can better assess your internet speed and identify any potential issues with your connection.